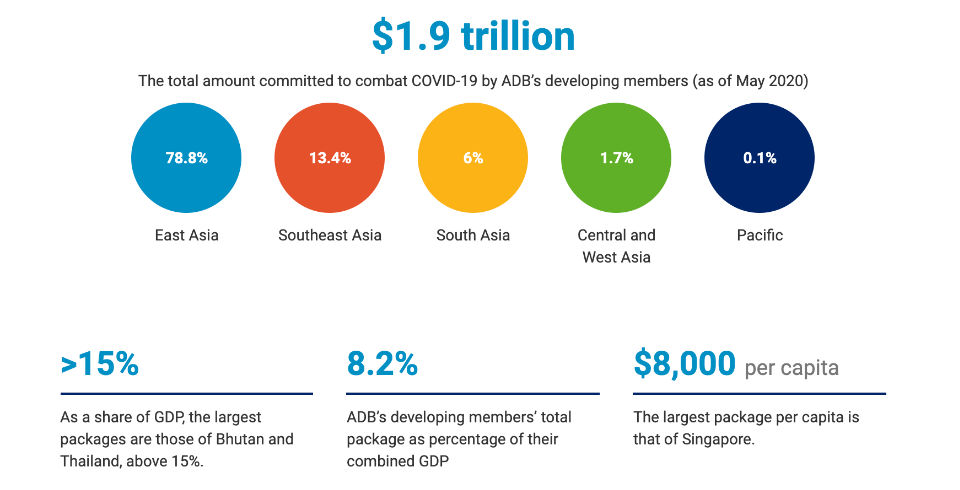
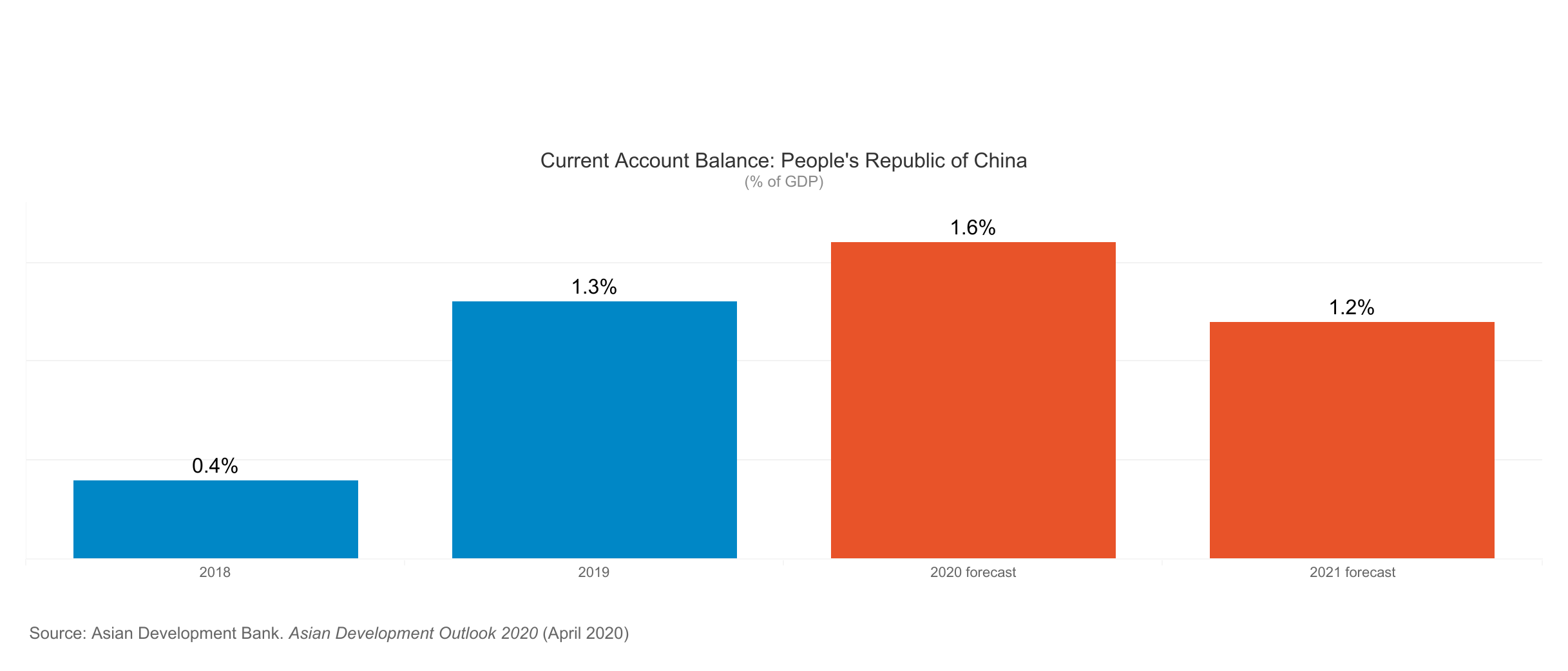
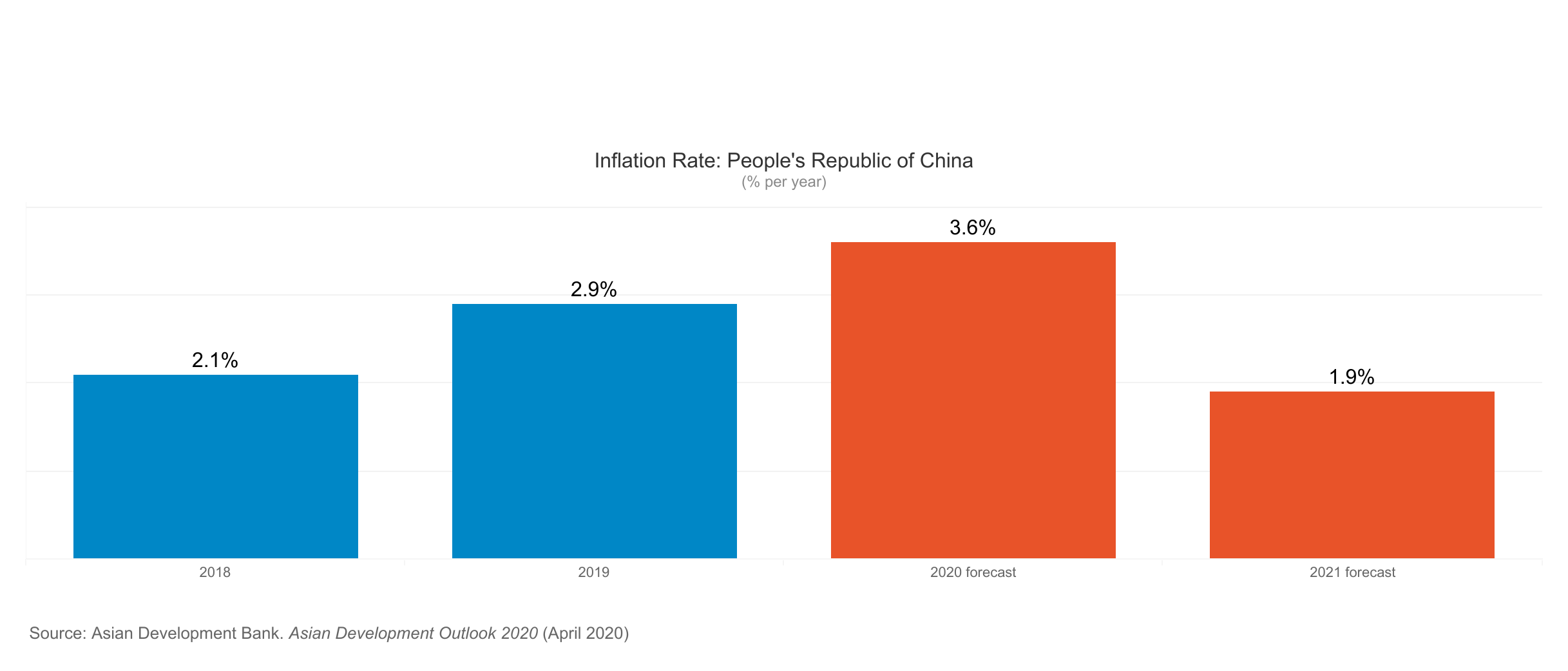
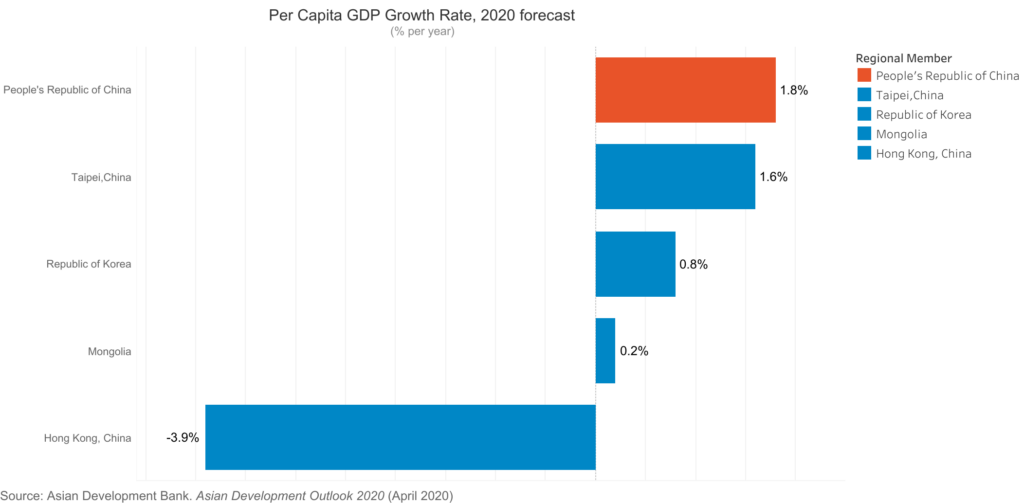
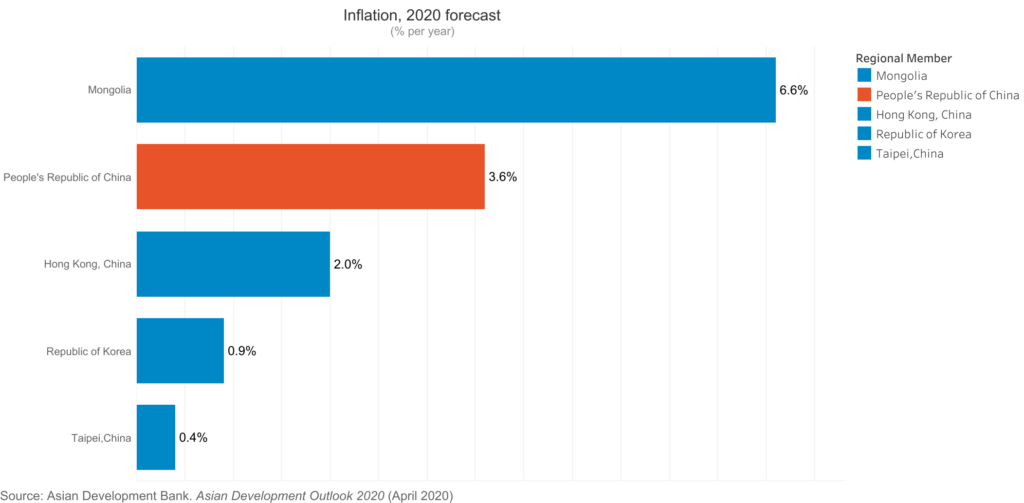
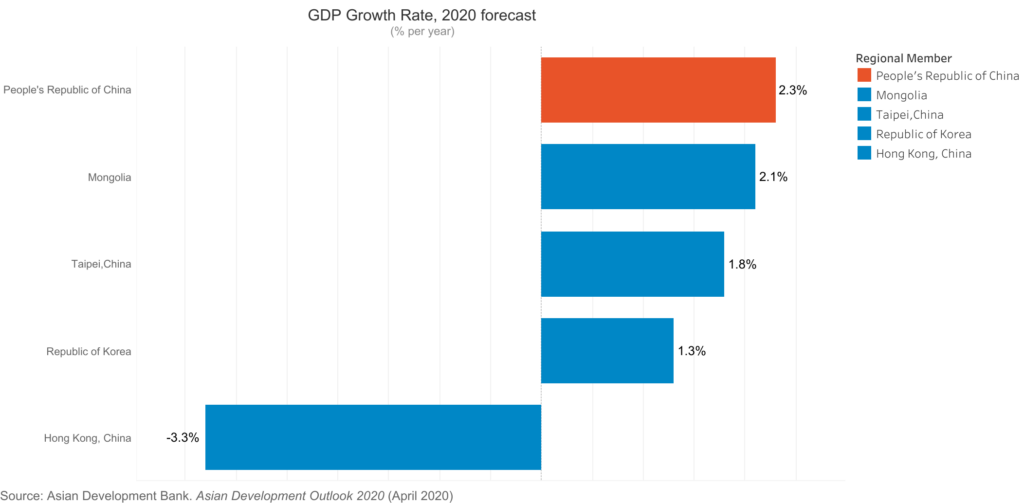
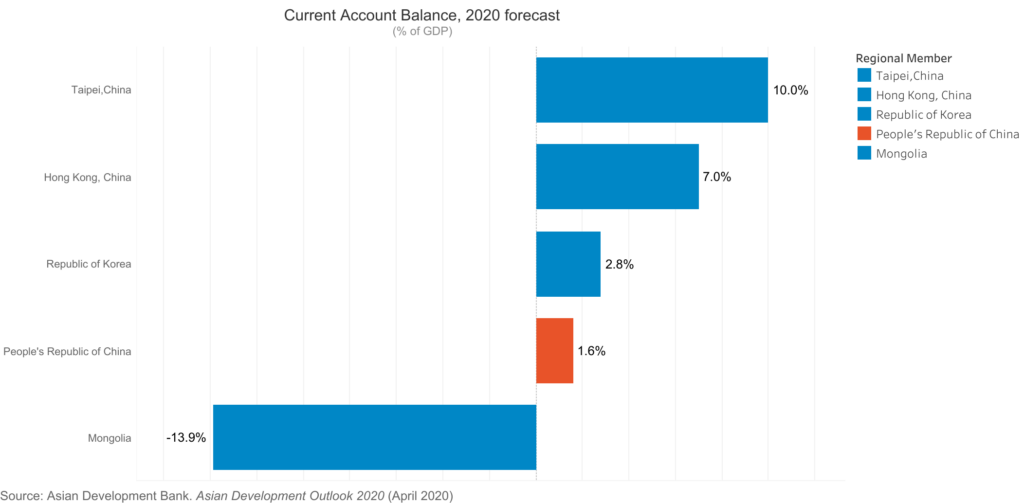
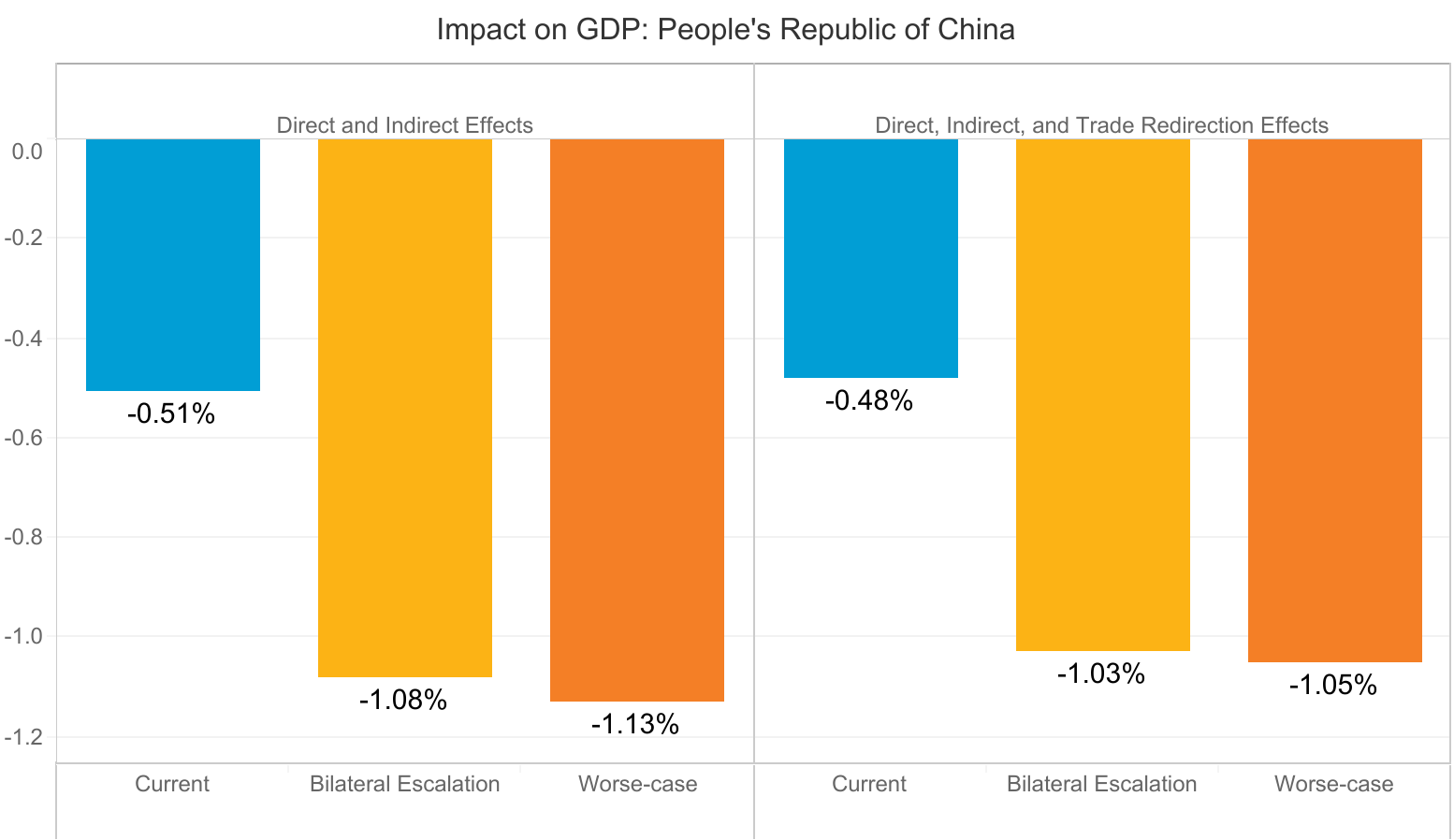
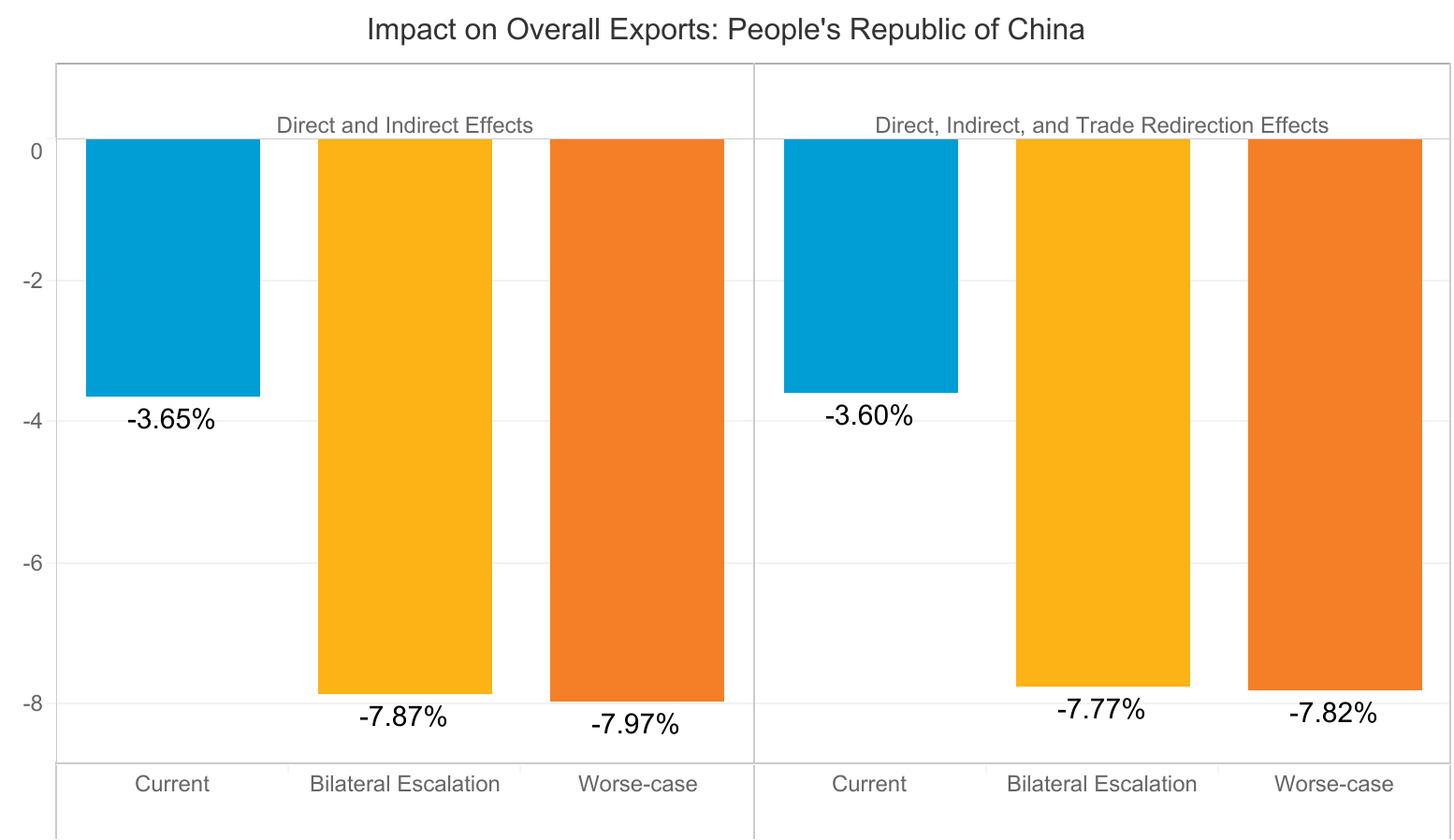
According to the Asian Development Bank the global economy could suffer between USD5.8 trillion and USD8.8 trillion in losses—equivalent to 6.4% to 9.7% of global gross domestic product (GDP)—as a result of the Corona Virus pandemic.
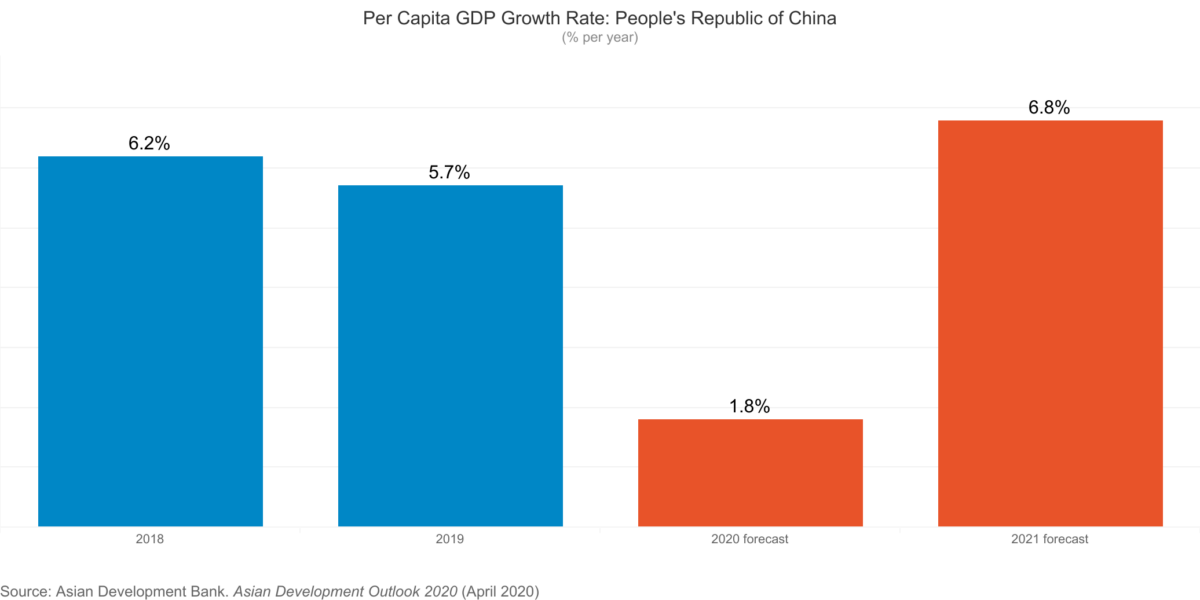
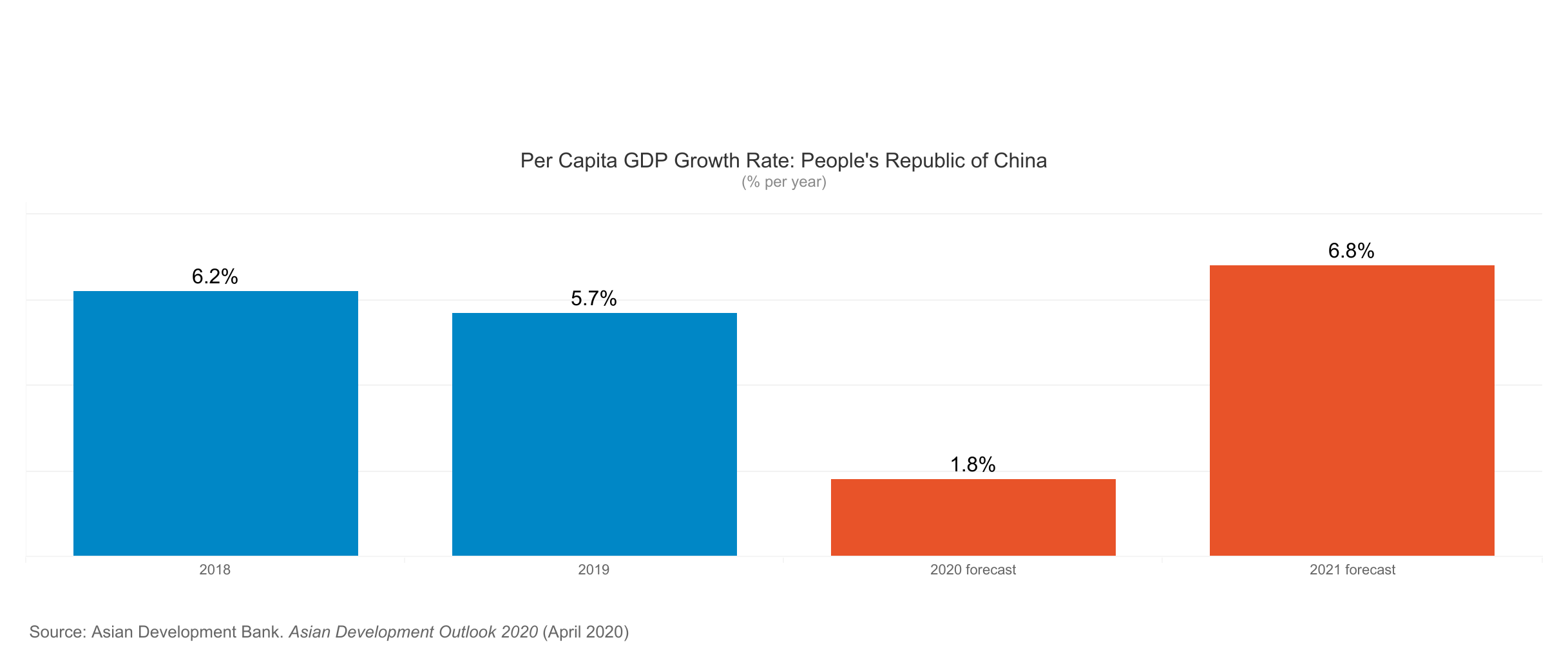
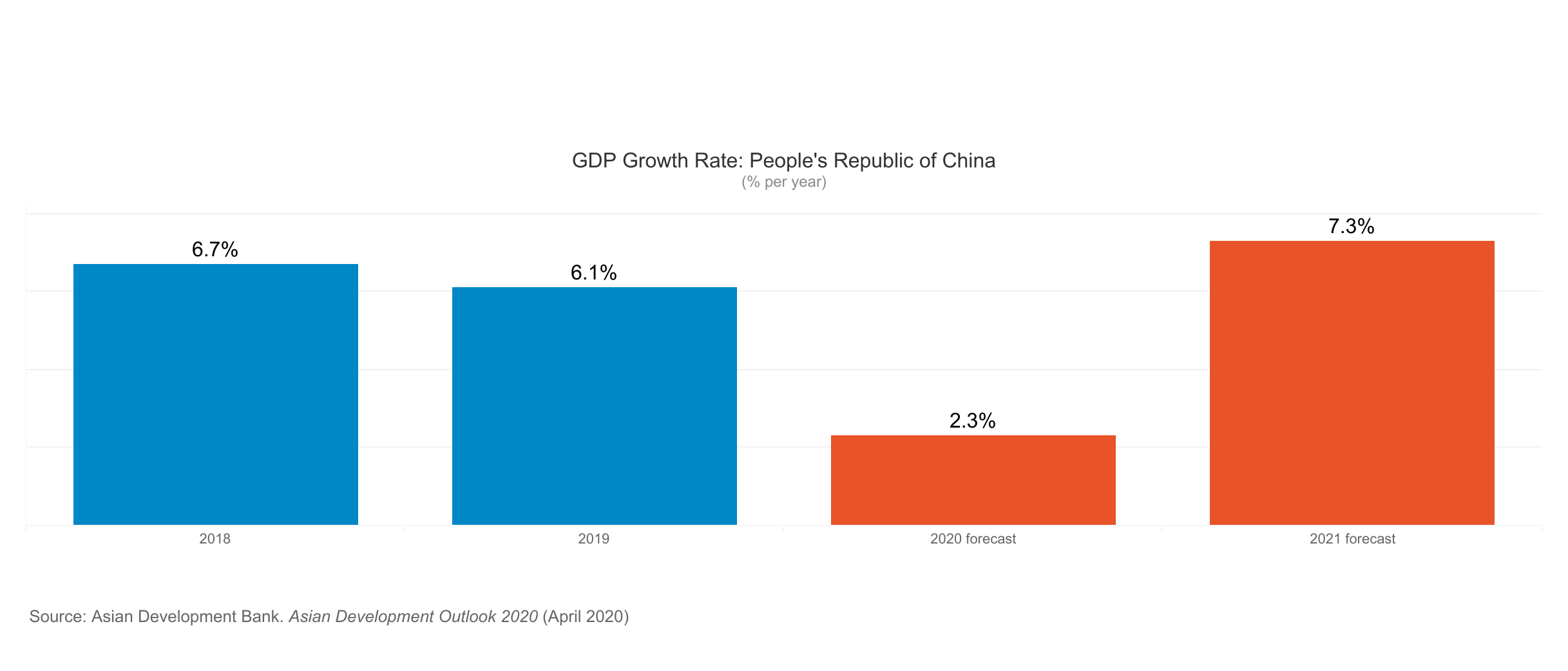
The report finds that economic losses in Asia and the Pacific could range from USD1.7 trillion under a short containment scenario of 3 months to USD2.5 trillion under a long containment scenario of 6 months, with the region accounting for about 30% of the overall decline in global output. The People’s Republic of China (PRC) could suffer losses between USD1.1 trillion and USD1.6 trillion.
Governments around the world have been quick in responding to the impacts of the pandemic, implementing measures such as fiscal and monetary easing, increased health spending, and direct support to cover losses in incomes and revenues. Sustained efforts from governments focused on these measures could soften COVID‑19’s economic impact by as much as 30% to 40%, according to the report. This could reduce global economic losses due to the pandemic to between $4.1 trillion and $5.4 trillion.
The analysis, which uses a Global Trade Analysis Project-computable general equilibrium model, covers 96 outbreak-affected economies with over 4 million COVID-19 cases. In addition to shocks to tourism, consumption, investment, and trade and production linkages covered in the ADO 2020 estimates, the new report includes transmission channels such as the increase in trade costs affecting mobility, tourism, and other industries; supply-side disruptions that adversely affect output and investment; and government policy responses that mitigate the effects of COVID-19’s global economic impact.
Under the short and long containment scenarios, the report notes that border closures, travel restrictions, and lockdowns that outbreak-affected economies implemented to arrest the spread of COVID-19 will likely cut global trade by $1.7 trillion to $2.6 trillion. Global employment decline will be between 158 million and 242 million jobs, with Asia and the Pacific comprising 70% of total employment losses. Labor income around the world will decline by $1.2 trillion to $1.8 trillion—30% of which will be felt by economies in the region, or between $359 billion and $550 billion.
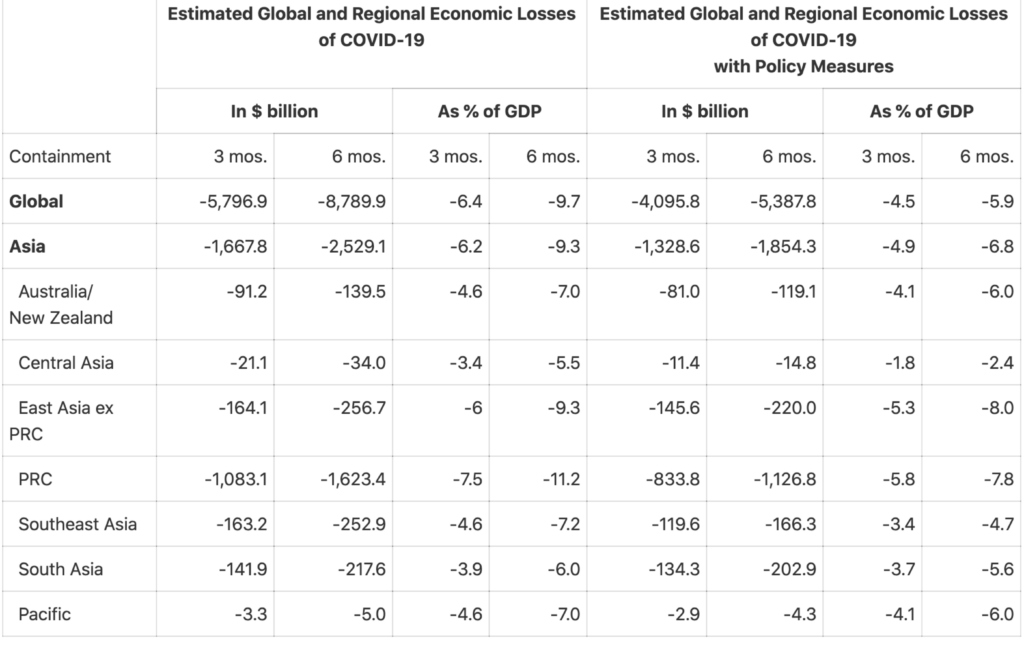
Source: ADB staff estimates.
Note: The 3-month and 6-month containment periods assumed in the scenarios are country-specific. They are the assumed time needed for a country to get a domestic outbreak under control from when the outbreak intensifies and start normalizing economic activity.
Apart from increasing health spending and strengthening health systems, strong income and employment protection are essential to avoid a more difficult and prolonged economic recovery. Governments should manage supply chain disruptions; support and deepen e-commerce and logistics for the delivery of goods and services; and fund temporary social protection measures, unemployment subsidies, and the distribution of essential commodities—particularly food—to prevent sharper falls in consumption, the report says.